Big hopes for muscle-like material
Unique physical properties found in Ras Labs synthetic muscle has drawn the interest of prosthetics makers and hospitals.
What it does
The engineered material has yet to be shaped into usuable forms. Its properties:

How it works

When a current is run through the gel, it contracts like a flexed muscle.

When the current is reversed, it expands.
On the drawing board ...
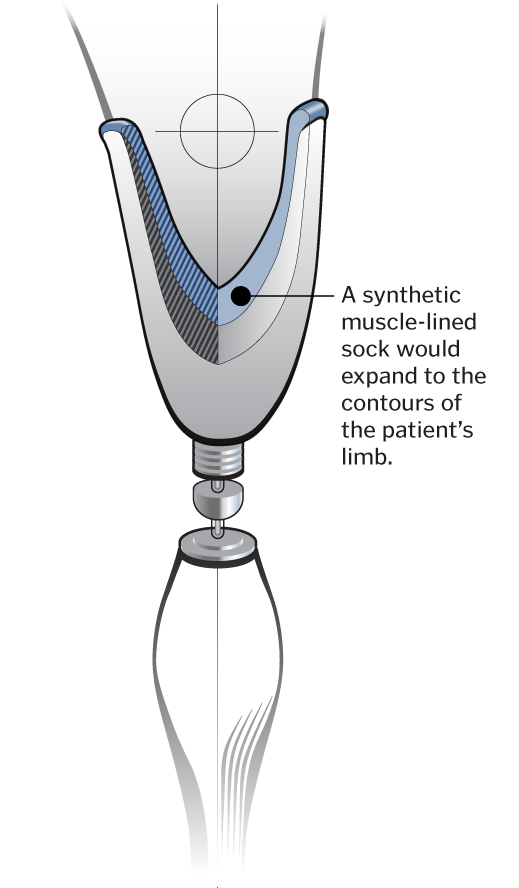
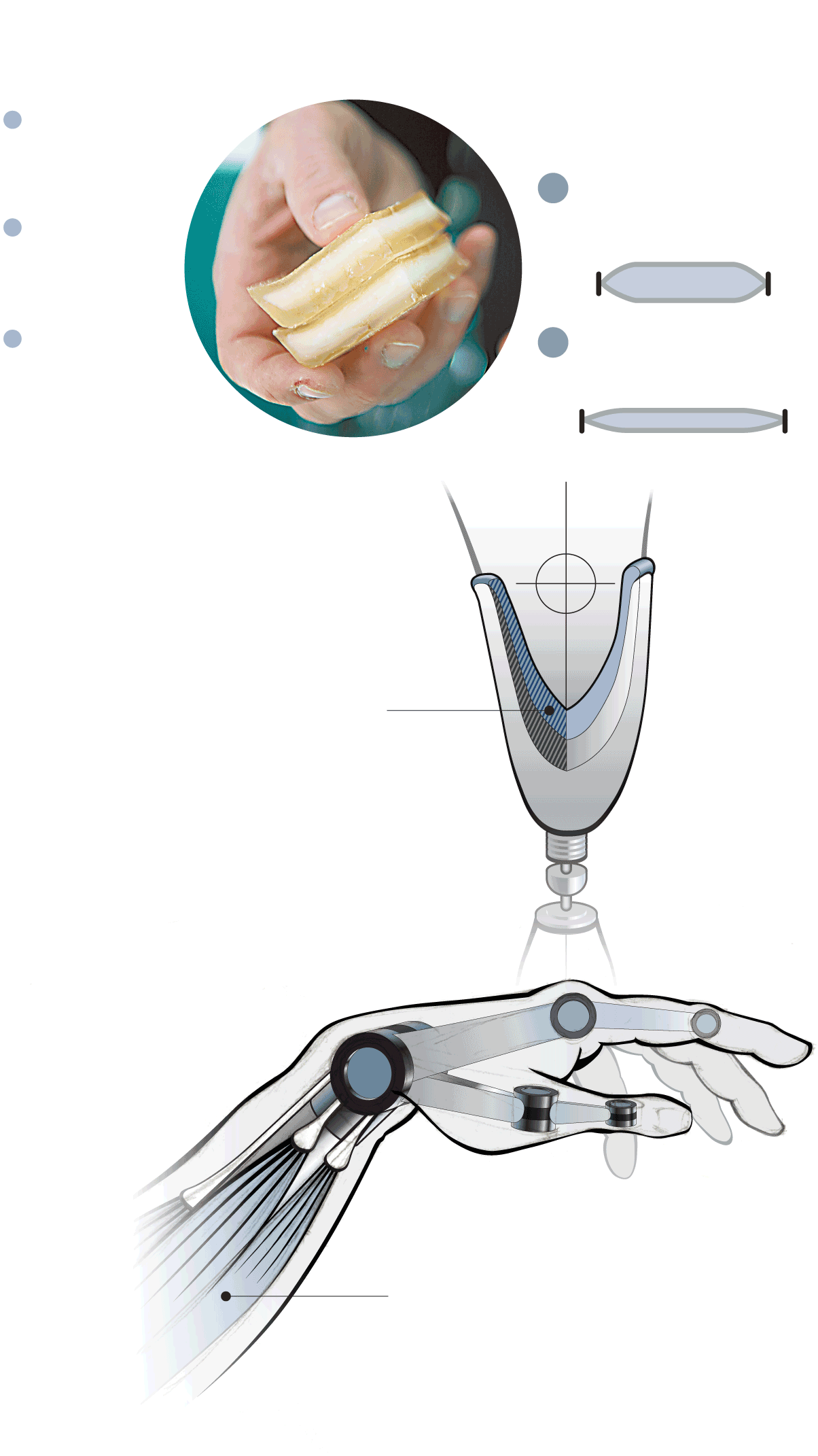
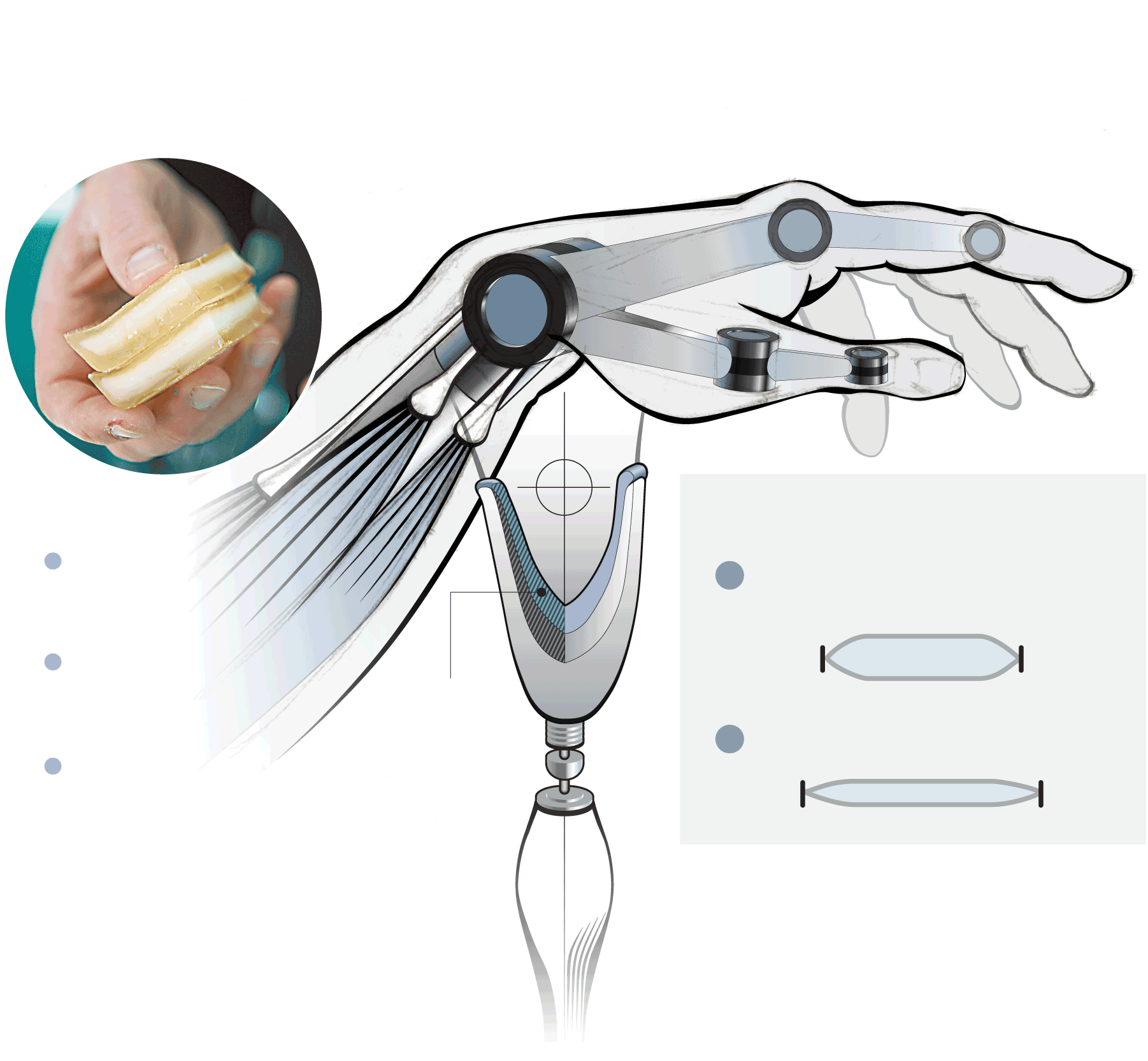
Although the artificial muscles exists only in the lab right now, improving the fit and comfort of prosthetic liners is seen as a first step.
Down the road ...
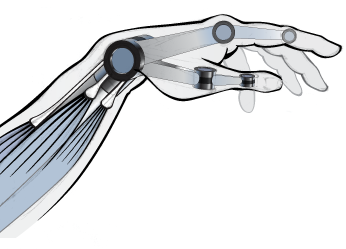
Lenore Rasmussen hopes it can be shaped into artificial muscles that can help operate more sophisticated and functional arm and hand prostheses.
What it does
The engineered material has yet to be shaped into usuable forms. Its properties:
It is resilient at extreme temperatures.
How it works
1
When a current is run through the gel, it contracts like a flexed muscle.
The gel can be rehydrated if it dries out.
It expands and contracts when electricity is run through it.
2
When the current is reversed, it expands.
On the drawing board ...
Although the artificial muscles exists only in the lab right now, improving the fit and comfort of prosthetic liners is seen as a first step.
A synthetic muscle-lined sock would expand to the contours of the patient’s limb.
Down the road ...
Lenore Rasmussen hopes it can be shaped into artificial muscles that can help operate more sophisticated and functional arm and hand prostheses.
Synthetic muscle
What it does
On the drawing board ...
Down the road ...
The engineered material has yet to be shaped into usuable forms. Its properties:
Although the artificial muscles exists only in the lab right now, improving the fit and comfort of prosthetic liners is seen as a first step.
Lenore Rasmussen hopes it can be shaped into artificial muscles that can help operate more sophisticated and functional arm and hand prostheses.
How it works
It is resilient at extreme temperatures.
1
When a current is run through the gel, it contracts like a flexed muscle.
The gel can be rehydrated if it dries out.
A synthetic muscle-lined sock would expand to the contours of the patient’s limb.
2
When the current is reversed, it expands.
It expands and contracts when electricity is run through it.
James Abundis / Globe Staff